apical lung hernia
Apical lung hernias typically manifest as unilateral right-sided air radiolucencies at the thoracic inlet on chest radiographs and can cause lateral tracheal deviation. This case serves to.
Sometimes the diagnosis can only be made with a Valsalva maneuver which accentuates the herniation improving its visibility on physical examination.
. This condition as a natural congenital occurrence is rareless than one in five cases reported. This patient was hospitalized with community acquired pneumonia and required nocturnal CPAP for. A lung hernia refers to part of a lung pushing through a tear or bulging through a weak spot in the chest wall neck passageway or diaphragm.
Symptoms when reported tend to be due to extrinsic pressure from the hernia on neck structures eg. Dysphagia oesophageal or coughing trachea 2. Apical lung hernias are often asymptomatic 1-3.
They are frequently intermittent and can cause lateral tracheal deviation. The remainder appear through the chest wall. Hernia of the lung occurs infrequently and not all of those that do occur cause symptoms that require treatment.
Dysphagia esophageal or coughing trachea 2. Herniation occurs through a defect in the Sibsons fascia and the apical segment of the lung protrudes in between the scalenus anterior and sternocleidomastoid muscles. The term pathological hernia is used to describe lung herniation induced by conditions such as tuberculosis focal bacterial infections empyema or osteomyelitis and malignant diseases 1.
Lung herniation has been described in association with congenital thoracic abnormalities and elevated intra-thoracic pressure such as trauma. In our patient this defect may be attributed to her chronic cough resulting in tearing of the Sibsons fascia. To the Editor.
In rare instances a lung hernia may become strangulated. We performed this study to characterize the clinical and radiologic manifestations of apical lung hernias. CONCLUSION Apical lung hernias typically manifest as unilateral right-sided air radiolucencies.
In our experience supraclavicular herniation of the lung is not unusual. No previous reports have documented spontaneous apical lung herniation in patients with EDS. A few increase progressively in size until they are large.
They are frequently intermittent and. Apical lung hernia is a rare variety and has been confined to few case reports and series. Sometimes the diagnosis can only be made with a Valsalva manoeuvre which accentuates the herniation improving its visibility on physical examination.
Symptoms when reported tend to be due to extrinsic pressure from the hernia on neck structures eg. Some lung hernias are congenital but trauma is the most common cause. The indications for surgery depend upon the severity of symptoms.
Subsequent computerised tomography CT scanning during a Valsalva manoeuvre demonstrated a large apical lung hernia arising through the costo-vertebral fascia into the root of the neck. My attention was drawn to the Snapshot of an apical lung hernia published in the Journal last year1 The full article is accessible to AMA members and paid subscribers. Jyotsna M Joshi MD.
Respiratory Medicine BYL Nair Hospital and Topiwala National Medical College Mumbai Maharashtra India. Login to read more or purchase a subscription now. Apical lung hernia is a rare variety and has been confined to few case reports and series.
OBJECTIVE We performed this study to characterize the clinical and radiologic manifestations of apical lung hernias. About half of all lung hernias however appear after trauma to the chest 5. We report a case of apical lung herniation through the superior thoracic aperture of an obese child using nocturnal CPAP.
This soft expansile mass is actually due to increased protrusion of the lung through the superior thoracic aperture and is regarded as pulmonary apical herniation. Most people who experience a lung hernia suffered a severe trauma such as a traffic accident in which. Herniation occurs through a defect in the Sibsons fascia and the apical segment of the lung protrudes in between the scalenus anterior and sternocleidomastoid muscles.
Respiratory Medicine BYL Nair Hospital and Topiwala National Medical College Mumbai Maharashtra India. Apical lung hernias are often asymptomatic 1-3. Apical lung hernias typically manifest as unilateral right-sided air radi- olucencies at the thoracic inlet on chest radiographs.
Repair by direct suture can be used for small tears in Sibsons costovertebral fascia while larger. Some hernias of the lung however are symptomatic being accompanied by local pain paroxysmal coughing hemoptysis or any combination of the three. The size and site of the lesion led to diagnostic uncertainty.
Jyotsna M Joshi MD. Conclusion Apical lung hernias typically manifest as unilateral right-sided air radiolucencies at the thoracic inlet on chest radiographs. Apical lung hernia.
The Medical Journal of Australia 01 Sep 2007 1876. Lung hernias occur in the cervical position in about one third of cases.
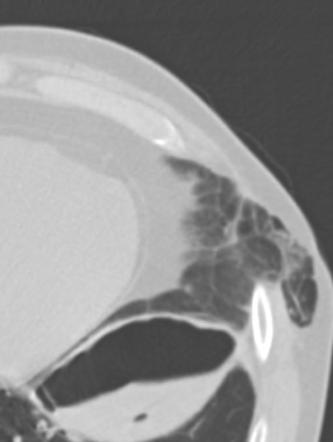
Intercostal Lung Hernia Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
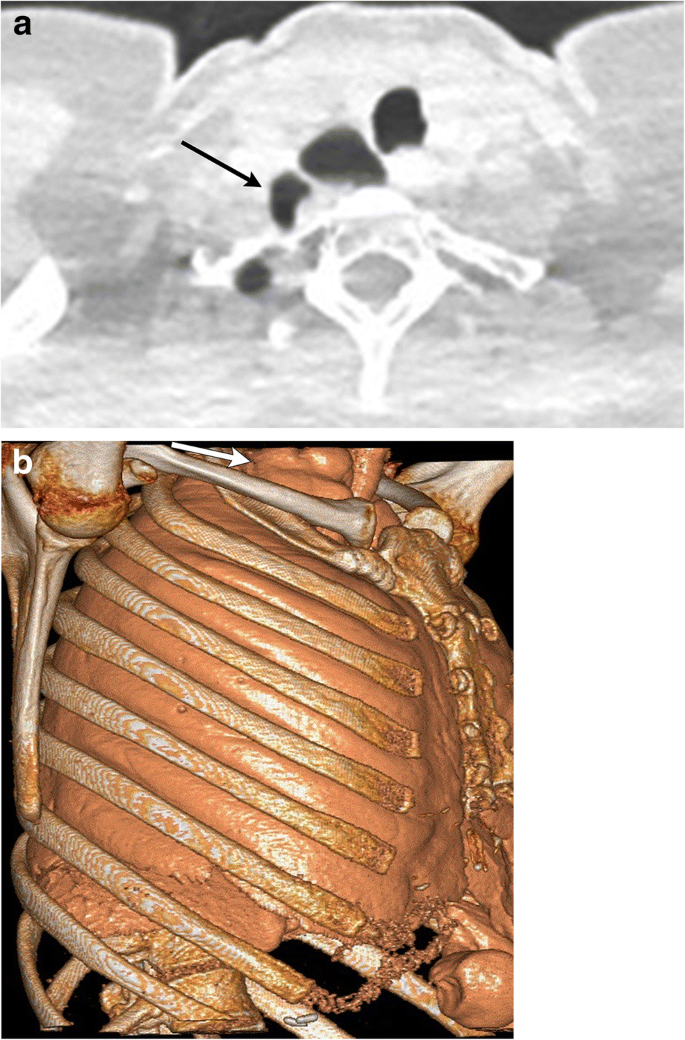
Imaging Of Thoracic Hernias Types And Complications Springerlink
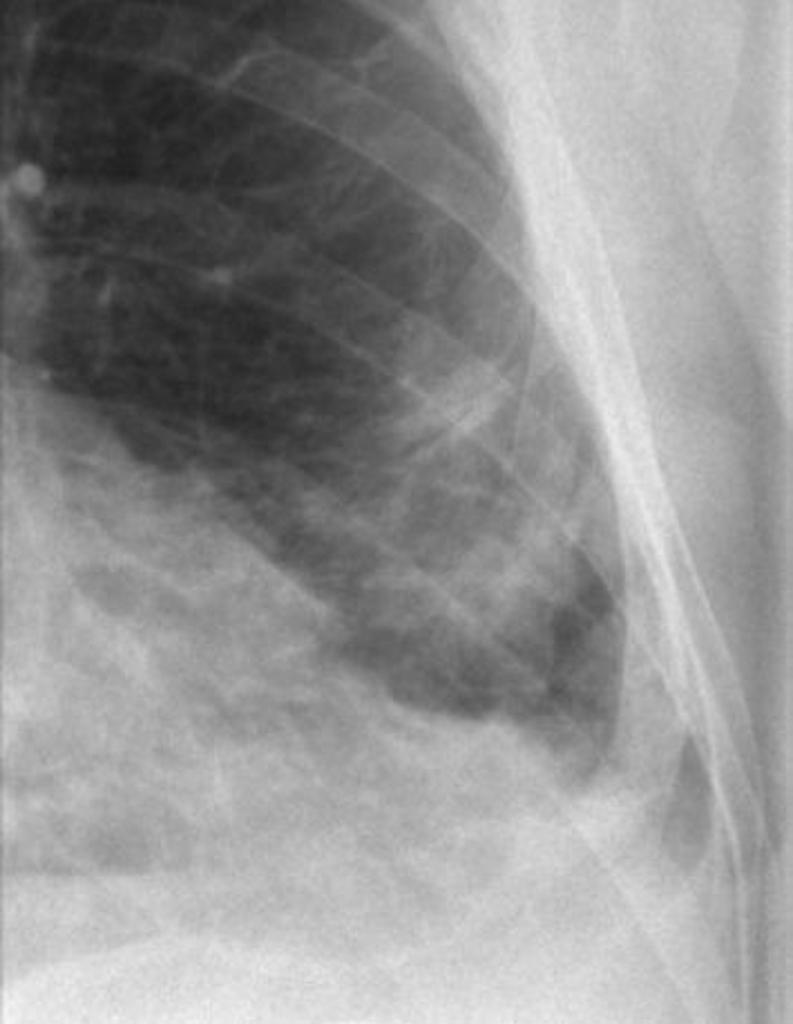
Intercostal Lung Hernia Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org

Pdf Adult Cervical Lung Herniation Importance Of Valsalva Manoeuvre In Imaging Semantic Scholar

Pdf Adult Cervical Lung Herniation Importance Of Valsalva Manoeuvre In Imaging Semantic Scholar
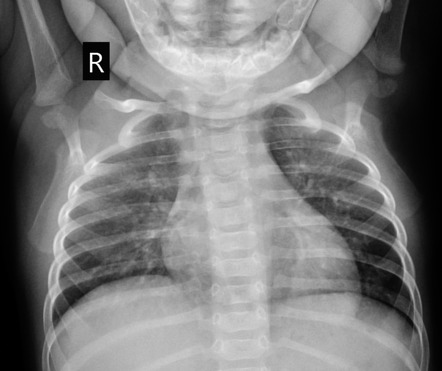
Cervical Lung Hernia Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Lung Hernia Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
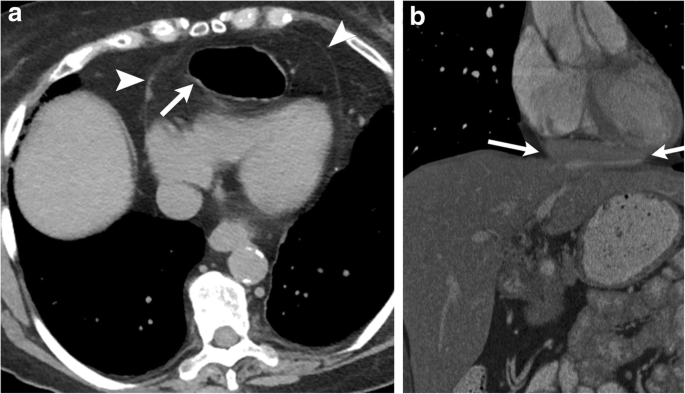
Imaging Of Thoracic Hernias Types And Complications Springerlink
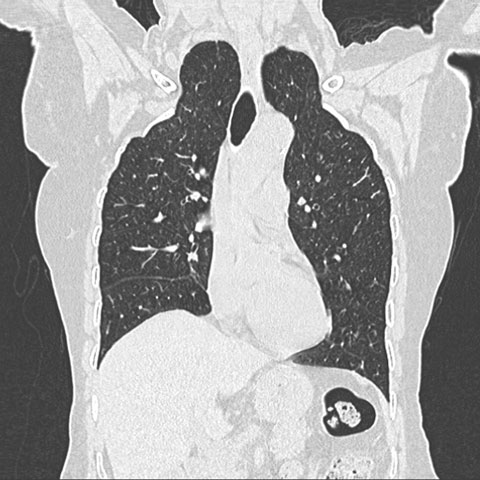
Apical Lung Hernia The Medical Journal Of Australia

Hiatal Hernia On Focused Cardiac Ultrasound Nephropocus

Hiatal Hernia On Focused Cardiac Ultrasound Nephropocus

Bilateral Cervical Lung Hernia With T1 Nerve Compression The Annals Of Thoracic Surgery
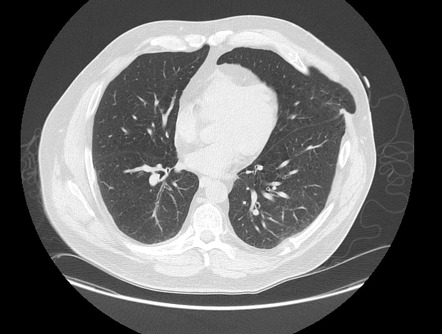
Lung Hernia Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Comments
Post a Comment